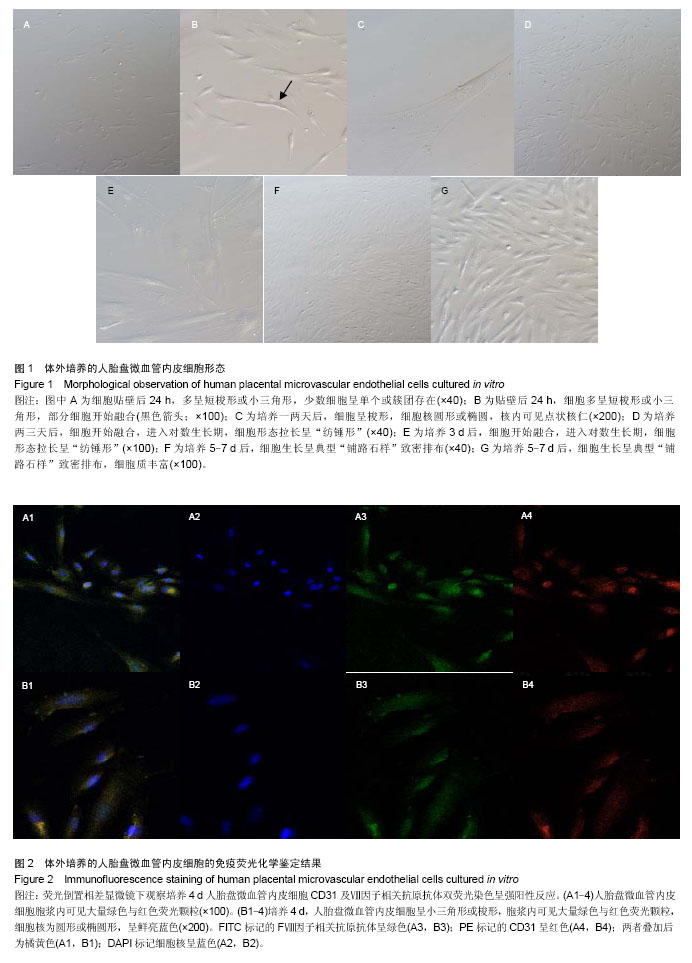
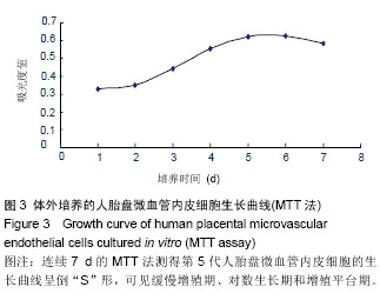
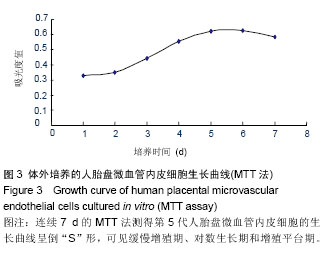
| [1] Dunk CE, Roggensack AM, Cox B, et al. A distinct microvascular endothelial gene expression profile in severe IUGR placentas. Placenta. 2012;33(4):285-293. [2] Qian-hua W, Shao-ping Z, Jian-wen Z, et al. Reduced expression of netrin-1 isassociated with fetal growth restriction. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;350(1-2):81-87. [3] Stefulj J, Panzenboeck U, Becker T, et al. Human endothelial cells of the placental barrier efficiently deliver cholesterol to the fetal circulation via ABCA1 and ABCG1. Circ Res. 2009; 104(5):600-608. [4] Absi M, Bruce JI, Ward DT. The Inhibitory Effect of simvastatin and aspirin on histamine responsiveness in human vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014.[5] Fazeli B, Rafatpanah H, Ravari H, et al. Sera of patients with thromboangiitis obliterans activated cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and changed their adhesive properties. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014;17(1):106-112. [6] Hirooka T, Yamamoto C, Yasutake A, et al. Expression of VEGF-related proteins in cultured human brain microvascular endothelial cells and pericytes after exposure to methylmercury. J Toxicol Sci. 2013;38(6):837-845. [7] Dye JF, Vause S, Johnston T, et al. Characterization of cationic amino acid transporters and expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human placental microvascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2004;18(1): 125-127. [8] Sölder E, Böckle BC, Nguyen VA, et al. Isolation and characterization of CD133+CD34+VEGFR-2+CD45-fetal endothelial cells from human term placenta. Microvasc Res. 2012;84(1):65-73. [9] An P, Xue YX. Effects of preconditioning on tight junction and cell adhesion of cerebral endothelial cells. Brain Res. 2009; 1272:81-88. [10] Yan LF, Wei YN, Nan HY, et al. Proliferative phenotype of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells plays a critical role in the overexpression of CTGF in the bleomycin-injured rat. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2014;66(1):61-71. [11] Nguyen VA, Fürhapter C, Obexer P, et al. Endothelial cells from cord blood CD133+CD34+ progenitors share phenotypic, functional and gene expression profile similarities with lymphatics. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(3):522-534. [12] Murthi P, So M, Gude NM, et al. Homeobox genes are differentially expressed in macrovascular human umbilical vein endothelial cells and microvascular placental endothelial cells. Placenta. 2007;28(2-3):219-223. [13] Leach L, Bhasin Y, Clark P, et al. Isolation of endothelial cells from human term placental villi using immunomagnetic beads. Placenta. 1994;15(4):355-364. [14] Challier JC, Kacemi A, Olive G. Mixed culture of pericytes and endothelial cells from fetal microvessels of the human placenta. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 1995;41(2): 233-241. [15] Kacemi A, Challier JC, Galtier M, et al. Culture of endothelial cells from human placental microvessels. Cell Tissue Res. 1996;283(2):183-190. [16] Kacémi A, Galtier M, Espié MJ, et al. Isolation of villous microvessels from the human placenta. C R Acad Sci III. 1997; 320(2):171-177. [17] 陈黎,梁志清,李俊男,等.人胎盘微血管内皮细胞体外原代培养及鉴定方法[J].第三军医大学学报,2006,28(9):907-909.[18] Ugele B, Lange F. Isolation of endothelial cells from human placental microvessels: effect of different proteolytic enzymes on releasing endothelial cells from villous tissue. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2001;37(7):408-413. [19] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01.[20] 张小红,李玉红,许倩,等.人早孕绒毛滋养层细胞原代培养:差异贴壁法与消化排除法联合应用的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(28):5220-5223. [21] 黄华梅,罗洁芳,谢德明.人脐带内皮细胞与平滑肌细胞的分离培养特征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(37): 7397-7400.[22] Rohde LH, Janatpore MJ, McMaster MT, et al. Complementary expression of HIP, a cell-surface heparan sulfate binding protein, and perlecan at the human fetal-maternal interface. Biol Reprod. 1998;58(4):1075-1083. [23] Cronier L, Hervé JC, Délèze J, et al. Regulation of gap junctional communicationduring human trophoblast differentiation. Microsc Res Tech. 1997;38(1-2):21-28. [24] Herr F, Baal N, Reisinger K, et al. HCG in the regulation of placental angiogenesis. Results of an in vitro study. Placenta. 2007;28 Suppl A:S85-S93. [25] Wang Q, Zhu J, Zou L, et al. Role of axonal guidance factor netrin-1 in human placental vascular growth. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011;31(2):246-250. [26] Lang I, Schweizer A, Hiden U, et al. Human fetal placental endothelial cells have a mature arterial and a juvenile venous phenotype with adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation potential. Differentiation. 2008;76(10):1031-1043.[27] Lang I, Pabst MA, Hiden U,et al.Heterogeneity of microvascular endothelial cells isolated from human term placenta and macrovascular umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2003;82(4):163-173. [28] Nachman RL, Jaffe EA. Endothelial cell culture: beginnings of modern vascular biology. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(8):1037-1040. |